A team of astronomers have studied 16 supermassive black holes that are firing powerful beams into space, to track where these beams, or jets, are pointing now and where they were aimed in the past, as reported in our latest press release. Using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) National Radio Astronomical Observatory’s (NRAO) Very Large Baseline Array (VLBA), they found that some of the beams have changed directions by large amounts.
These two Chandra images show hot gas in the middle of the galaxy cluster Abell 478 (left) and the galaxy group NGC 5044 (right). The center of each image contains one of the sixteen black holes firing beams outwards. Each black hole is in the center of a galaxy embedded in the hot gas.
By mousing over the images, labels and the radio images appear. Ellipses show a pair of cavities in the hot gas for Abell 478 (left) and ellipses show two pairs of cavities for NGC 5044 (right). These cavities were carved out by the beams millions of years ago, giving the directions of the beams in the past. An X shows the location of each supermassive black hole.
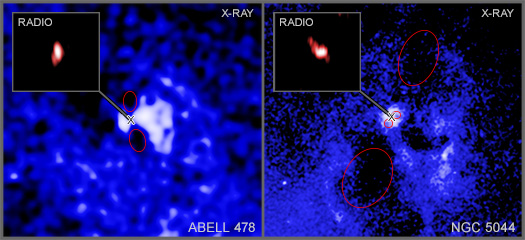
The VLBA images are shown as insets, which reveal where the beams are currently pointing, as seen from Earth. The radio images are both much smaller than the X-ray images. For Abell 478 the radio image is about 3% of the width of the Chandra image and for NGC 5044 the radio image is about 4% of the Chandra image’s width.
A comparison between the Chandra and VLBA images shows that the beams for Abell 478 changed direction by about 35 degrees and the beams for NGC 5044 changed direction by about 70 degrees.
Across the entire sample the researchers found that about a third of the 16 galaxies have beams that are pointing in completely different directions than they were before. Some have changed directions by nearly 90 degrees in some cases, and over timescales between one million years and a few tens of millions of years. Given that the black holes are of the order of 10 billion years old, this represents a relatively rapid change for these galaxies.

Black holes generate beams when material falls onto them via a spinning disk of matter and some of it then gets redirected outward. The direction of the beams from each of these giant black holes, which are likely spinning, is thought to align with the rotation axis of the black hole, meaning that the beams point along a line connecting the poles.
These beams are thought to be perpendicular to the disk. If material falls towards the black holes at a different angle that is not parallel to the disk, it could affect the direction of the black hole’s rotation axes, changing the direction of the beams.
Scientists think that beams from black holes and the cavities they carve out play an important role in how many stars form in their galaxies. The beams pump energy into the hot gas in and around the galaxy, preventing it from cooling down enough to form huge numbers of new stars. If the beams change directions by large amounts, they can tamp down star formation across much larger areas of the galaxy.
The paper describing these results was published in the January 20th, 2024 issue of The Astrophysical Journal, and is available here. The authors are Francesco Ubertosi (University of Bologna in Italy), Gerritt Schellenberger (Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian), Ewan O’Sullivan (CfA), Jan Vrtilek (CfA), Simona Giacintucci (Naval Research Laboratory), Laurence David (CfA), William Forman (CfA), Myriam Gitti (University of Bologna), Tiziana Venturi (National Institute of Astrophysics—Institute of Radio Astronomy in Italy), Christine Jones (CfA), and Fabrizio Brighenti (University of Bologna).
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science from Cambridge Massachusetts and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
This image contains two X-ray images presented side by side, separated by a thin, gray line. On the left is an image of galaxy cluster Abell 478, and on the right is an image of galaxy group NGC 5044.
The X-ray image of Abell 478 resembles a gooey, blue substance that has been spilled on a black canvas. Most of the image is covered in this blue goo texture, which is hot gas in X-ray light, however there are cavities where no blue texture is present. At the center of the image is a bright, white region. Within the white region, too small to identify, exists Abell 478's supermassive black hole.
The X-ray image of NGC 5044, on our right, is more pixelated than the image of Abell 478. It resembles blue television static or noise, that is present on a television when no transmission signal is detected. Most of the image is covered in this blue static, however there are cavities where no blue static is present. At the center of the image is a bright, white region. Within the white region, too small to identify, exists NGC 5044's supermassive black hole.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||