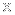A jet from a very distant black hole being illuminated by the leftover glow from the Big Bang
Jets in the early Universe such as this one, known as B3 0727+409, give astronomers a way to probe the growth of black holes at a very early epoch in the cosmos. The light from B3 0727+409 was emitted about 2.7 billion years after the Big Bang when the Universe was only about one fifth of its current age.
This main panel graphic shows Chandra's X-ray data that have been combined with an optical image from the Digitized Sky Survey. (Note that the two sources near the center of the image do not represent a double source, but rather a coincidental alignment of the distant jet and a foreground galaxy.)
The inset shows more detail of the X-ray emission from the jet detected by Chandra. The length of the jet in 0727+409 is at least 300,000 light years. Many long jets emitted by supermassive black holes have been detected in the nearby Universe, but exactly how these jets give off X-rays has remained a matter of debate. In B3 0727+409, it appears that the CMB is being boosted to X-ray wavelengths.
Scientists think that as the electrons in the jet fly from the black hole at close to the speed of light, they move through the sea of CMB radiation and collide with microwave photons. This boosts the energy of the photons up into the X-ray band to be detected by Chandra. If this is the case, it implies that the electrons in the B3 0727+409 jet must keep moving at nearly the speed of light for hundreds of thousands of light years.
The significance of this discovery is heightened because astronomers essentially stumbled across this jet while observing a galaxy cluster in the field. Historically, such distant jets have been discovered in radio waves first, and then followed up with X-ray observations to look for high-energy emission. If bright X-ray jets can exist with very faint or undetected radio counterparts, it means that there could be many more of them out there because astronomers haven't been systematically looking for them.
A paper describing these results was published in the 2016 January 1st issue of The Astrophysical Journal Letters and is available online. The authors are Aurora Simionescu (Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Kanagawa, Japan), Lukasz Stawarz (Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland), Yuto Ichinohe (Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Kanagawa, Japan), Teddy Cheung (Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC), Marek Jamrozy (Jagiellonian University, Kraków, Poland), Aneta Siemiginowska (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MA), Kouichi Hagino (Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Kanagawa, Japan), Poshak Gandhi (University of Southampton, Southampton, UK) and Norbert Werner (Stanford University, Stanford, CA).
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Chandra program for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts, controls Chandra's science and flight operations.
The image features a black hole named B3 0727+409 in the center of the full frame, and with a pullout in the upper right. The black hole is surrounded by small bright spots of light, mostly distant galaxies and foreground stars. The colors in the image are predominantly blue, pale yellow, black and white. The main panel graphic shows Chandra X-ray Observatory data in blue that have been combined with an optical image from the Digitized Sky Survey (pale yellow and white). There are two sources near the center of the image that do not represent a double source, but rather a coincidental alignment of the distant jet and a foreground galaxy. The inset shows more detail of the X-ray emission from a long jet detected by Chandra. The length of the jet in 0727+409 is at least 300,000 light years. Many long jets emitted by supermassive black holes have been detected in the nearby Universe, but exactly how these jets give off X-rays has remained a matter of debate.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||